The JTC Network Our Legacy & Foundation
Before the launch of the Jurat Protocol and our pivot to EVM-based tooling, we pioneered legal recourse on Bitcoin through the Jurat Transaction Chain (JTC)—an innovative fork of Bitcoin that introduced court-enforceable transactions and early experimentation with Bitcoin Ordinals. Explore how our work on JTC laid the groundwork for on-chain legal enforcement.
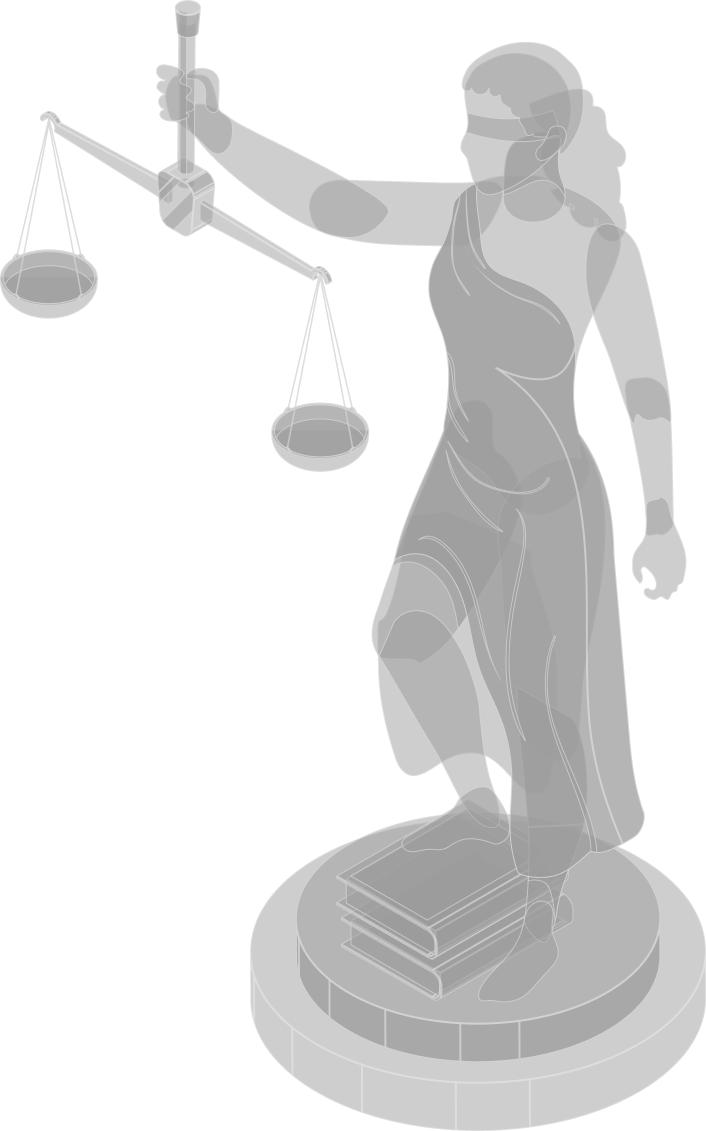

What was the JTC Network?
The Jurat Transaction Chain (JTC) was the original, pioneering implementation of Jurat’s mission: enabling real-world legal enforcement on-chain. Launched as a custom Bitcoin fork, the JTC network was a proof of concept designed to show that blockchain transactions could be subject to formal legal processes—without sacrificing decentralization or immutability.
Unlike typical chains, JTC introduced a native legal enforcement mechanism at the protocol level. This meant that courts could issue binding rulings—such as asset freezes or ownership determinations—and those rulings could be executed directly on-chain through special judicial transactions. These transactions were verified by nodes only when they were accompanied by authenticated court documentation.
The system worked by embedding legal logic into Bitcoin’s core consensus layer, allowing miners and nodes to accept certain state changes only if they conformed to a valid court order, verified via cryptographic signatures and affidavit metadata. These court-validated transactions were indistinguishable in immutability from any other Bitcoin transaction—they simply followed an additional layer of legal validation.
By combining Bitcoin’s well-known attributes of security, transparency, and censorship resistance with court-recognized legal workflows, JTC provided a groundbreaking demonstration:
Legal enforcement is not incompatible with decentralization.
Blockchains can protect consumer rights and comply with the law—without needing central intermediaries.
What JTC Accomplished
JTC was the first time a blockchain showed that real-world court rulings could be enforced on-chain in a fully transparent and auditable way.

Court-Enforced Transactions
JTC was the first blockchain to successfully execute legally binding state and federal court orders on-chain. This included the ability to freeze wallets, reverse stolen funds, and enforce asset recovery based on actual judicial decisions. ... Using a protocol-native mechanism, the network allowed legal outcomes to directly affect blockchain state changes—without requiring centralized control or hard forks. This was a critical breakthrough in proving that legal enforcement could coexist with immutability.
Affidavit-Based Transaction Proofing
To execute a court order on-chain, users submitted court-authenticated affidavits, which were embedded into the blockchain as part of the transaction metadata. These affidavits contained details ... about the ruling, case number, signatory, and jurisdiction. This created a transparent, cryptographic record of legal provenance directly on-chain. It marked the first time legal documents and factual determinations could become part of the blockchain’s historical record in a verifiable way.

Real-World Test Cases
Most importantly, JTC was not just theoretical. These early successes provided proof that real legal frameworks could be operationalized on-chain without compromising the decentralized nature of the system. ... These test cases served as the foundation for the more scalable, EVM-based system now being developed through the Jurat Protocol.

Bitcoin Ordinal Support
JTC also served as an experimental playground for Bitcoin-native NFTs and Ordinals, integrating inscription logic to test how non-financial data like digital art, legal documents, or titles could be managed within a compliant framework. ... While the core purpose of JTC was legal enforcement, this exploration demonstrated that even expressive, community-based use cases like NFTs could benefit from a legal backbone—offering potential solutions for copyright enforcement and provenance verification.
From JTC to the Jurat Protocol: Scaling Legal Enforcement in Web3
While the JTC network proved that legal enforcement on-chain was possible, its architecture as a Bitcoin fork limited its extensibility. That’s why the next iteration of our vision—the Jurat Protocol—has been purpose-built on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), where flexibility, composability, and integration are the standard. By translating the core legal principles proven on JTC into modular, interoperable tools, the Jurat Protocol now empowers developers, institutions, and users to bring real-world legal recourse to any Web3 application.
Modular Smart Contracts Instead of Protocol-Level Forking
Unlike JTC, which embedded legal logic into the core consensus of a blockchain fork, the Jurat Protocol uses EVM-compatible smart contracts to implement enforcement logic at the application layer. ... This modular approach means that any project can opt-in, rather than having to migrate to a new chain. Whether you're building a DAO, token, or DeFi protocol, you can integrate Jurat’s legal layer without changing your base infrastructure.
Integration with Ethereum and L2s Like Base
The Jurat Protocol is launching on Ethereum L1 for maximum security and Base L2 for low-cost scalability and compliance compatibility. This dual-layer deployment strategy allows enforcement actions— ... like court-ordered freezes, reversals, or arbitration outcomes—to be executed efficiently while preserving institutional-grade guarantees.Future expansion includes compatibility with Polygon zkEVM, Solana, and Avalanche Subnets, making Jurat’s enforcement layer truly multi-chain and composable across ecosystems.
Developer SDKs for dApps and Token Projects
We’re building a comprehensive Jurat SDK to make legal enforcement accessible to every Web3 developer. Through simple APIs and contract libraries, teams can embed logic into their applications ... to respond to verified legal orders, track dispute outcomes, or secure assets pending arbitration. The SDK also supports integration with wallets, exchanges, and token contracts—enabling a wide range of compliant financial primitives.
UI-First Arbitration and Dispute Resolution Tools
The Jurat Protocol includes intuitive, web-based tools like the Judicial Manager UI and Arbitration Dashboard, where users, courts, and arbitrators can submit claims, attach evidence, and track the status of their cases. ... Decisions—whether from a U.S. court, arbitration body, or community tribunal—are then translated into Jurat Litigation Codes (JLCs) for on-chain enforcement. These tools make navigating legal processes in Web3 as simple as using a traditional legal portal—only now decentralized.
Oracle Network as a Witness Layer
A key innovation of the Jurat Protocol is its decentralized Oracle Network, which acts as a witness—not a validator—for legal events. These oracles fetch and witness court orders from sources like PACER and Odyssey ... ensuring legal documents are authentic and eligible for on-chain execution. Unlike traditional oracles that validate data for pricing or randomness, Jurat’s oracles are designed to observe and attest to legal truths, respecting due process and maintaining decentralization.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Unlike standard NFTs, JTC Ordinal owners can enforce their real world legal rights in real world assets through Jurat’s decentralized court system bridge. The legal remedies that users gain access to with JTC Ordinals make them a more versatile option for tokenizing real-world assets.
Anyone can create tokenized assets with JTC Ordinals. The minting interface is simple and allows users to upload legal documents like a deed or a contract.
The tokenization market is moving forward. Projects are tokenizing assets like real estate and private securities. Even governments are getting involved, with central banks starting to create tokenized treasuries. Leading investment firms are funding research into how tokenization can be further integrated into financial markets.
Contact Us
Get In Touch
What People Are Saying About Us
One of the most innovative and visionary proposals… The revolutionary implications of having changing legal criteria acknowledged and acted upon through smart contracts is groundbreaking.
Once the mass population believes that their rights could be protected and enforced on the blockchain, the mainstream adoption of blockchain would be underway.
[Jurat] will provide a very strong competition to the ‘code is law’ philosophy when deciding whether to side with a court order or with a smart contract’s ‘blind justice’ by just doing what it was programmed to do.
